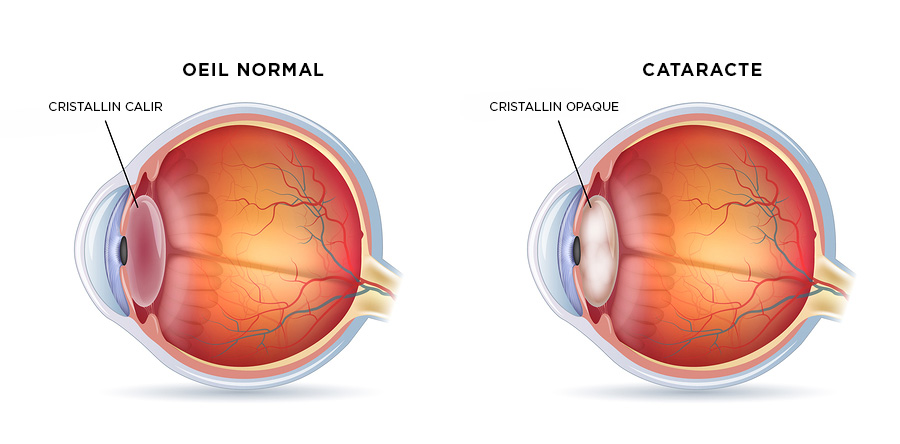
What is a cataract?
The lens is a small, normally transparent magnifying glass, located behind the pupil and which can gradually cloud for various reasons (age, trauma, inflammation, etc.). It’s the cataract. The lens plays a role in the optical balance of the eye; it allows light to reach the structures necessary for the perception of the image: the retina, the optic nerve..
Why and when to operate a cataract?
When the clouding of the lens, that is to say the cataract, becomes a discomfort to the vision for the daily or professional activities, the operation of the cataract makes it possible to improve the vision (provided that it does not there is no other pathology such as for example a disease of the optic nerve or of the retina which could possibly go unnoticed before the intervention).
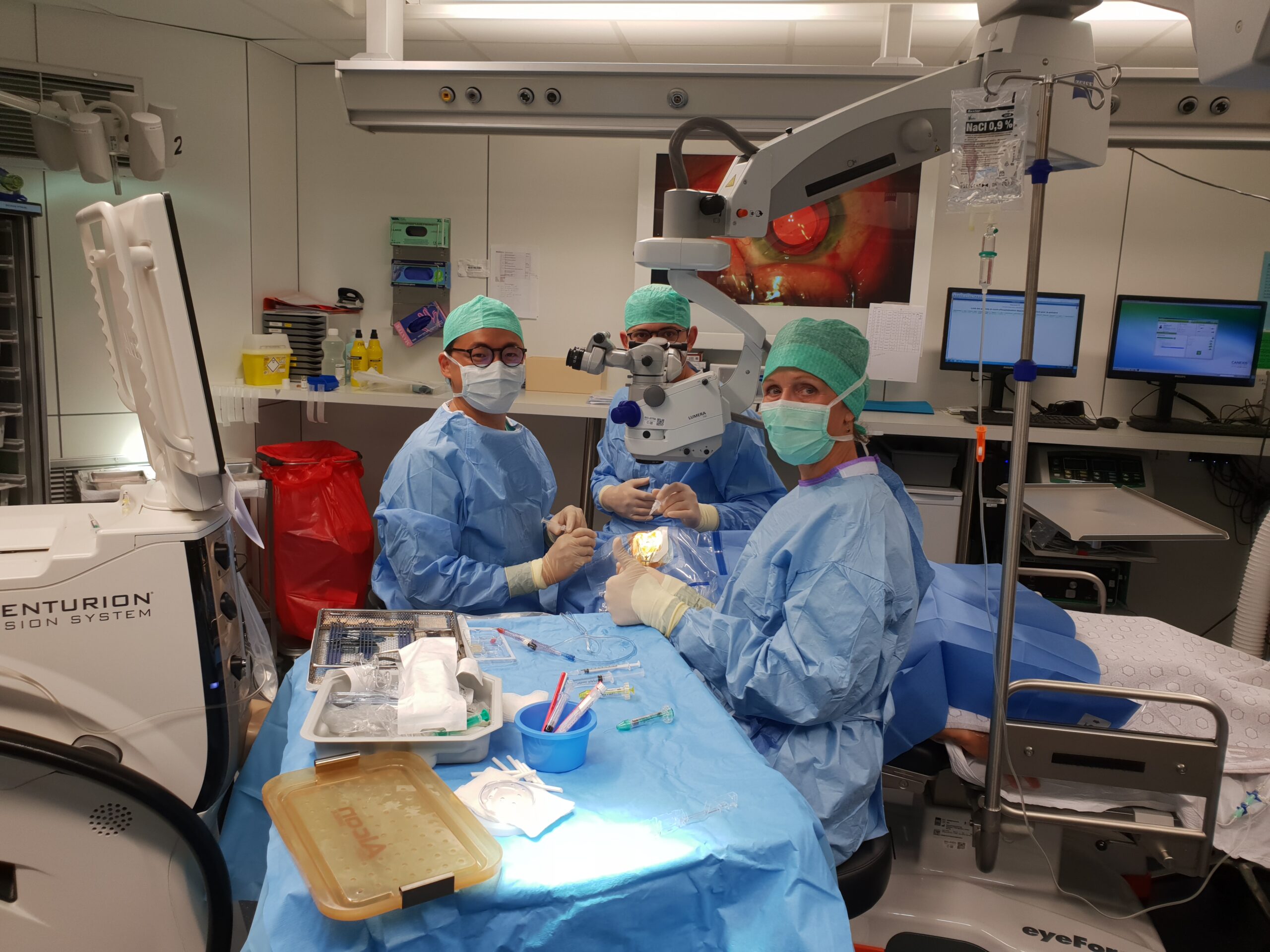
How is the cataract surgery performed?
The cataract intervention represents a precise ophthalmological surgical gesture; it consists in replacing the opaque content of the lens with a transparent implant. The patient is installed on the back in the operating room, in an environment where everything will be done to work in sterile conditions. The cataract procedure takes place under a microscope.
Where does the cataract operation take place and under what anesthesia?
The cataract operation is performed in day surgery (short stay not exceeding one day). Different types of anesthesia can be performed, most of the time it will be local anesthesia with drops accompanied by sedation. The two extremes being either general anesthesia or local anesthesia by instillation of drops in the eye. The choice of anesthesia depends on the ophthalmologist, taking into account if possible the wishes of the patient. Any anesthesia presents in itself a risk, this is why local anesthesia by drops is the most practiced.
Operative technique of cataract
During the cataract procedure, the contents of the lens are fragmented by ultrasound (phakoemulsification) and aspirated before being replaced by the implant. The incisions are most often self-sealing but sometimes have to be sutured. In the event of technical difficulties, the incision can be widened and the technique adopted in the particular case, until there is no possibility of placing an implant at the same time. This situation is, however, very rare. The placement of the implant cannot guarantee that the glasses will not be necessary afterwards.
Usual postoperative course after cataract surgery
A local treatment with eye drops or ointments is instituted after the intervention for a certain time. Glasses or a change of glasses are to be expected.
During this postoperative period the patient can lead a normal life (reading, office work, television, etc.) with a few exceptions:
- the eye must be protected from infectious agents during the healing period,
- driving a vehicle will only be authorized after sufficient visual recovery and in agreement with the ophthalmologist,
- it will be necessary to avoid lifting too heavy things, to handle dangerous instruments,
- it will also obviously be necessary to avoid rubbing the eyes or risking receiving a blow on the operated eye.
Source : SFO
CONTACT
You want to make an appointment? You can either call one of the 5 sites via the button below, or make an appointment directly online in the Contact section, or send me a message in the Contact section
The ophthalmology secretaries and Dr. Qin’s team are available to answer all your questions and requests for information in order to make the best choice. I will be pleased to welcome you at one of the 5 sites.
Discover the 5 sites

